Emotional And Behavioral Changes Caused By A Stroke

The effects of a stroke can be very serious, and the degree of disability varies from moderate to severe. However, there are other side effects that people do not think about so much, but which are just as important. Failure to address them can be devastating. We are talking about emotional and behavioral changes that patients sometimes experience after a stroke.
Neurorehabilitation after a stroke focuses more on restoring the patient’s motor skills. A stroke can cause hemiplegia, difficulty walking, aphasia, cognitive decline, etc. These side effects are the most common in a wide list of potential problems and require a lot of attention. However, if the patient does not receive help for their emotional and behavioral changes, their physical rehabilitation may not develop as expected.
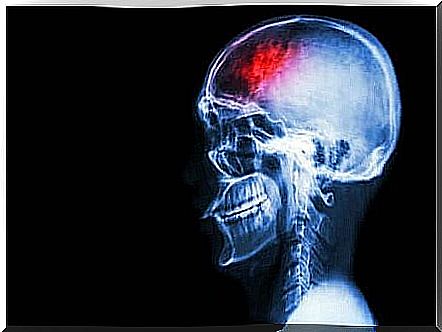
What is a stroke?
A stroke is a sudden interruption or reduction in the blood supply to the brain. It causes a combination of physical symptoms and cognitive changes that can be temporary or permanent.
Stroke affects 13 million people worldwide, and hundreds of thousands suffer from functional impairments as a result of stroke. The number of strokes is increasing. However, it is important to note that 90% of strokes can be prevented.
In Norway, 12,000 people are affected by stroke every year. Stroke is the third most common cause of death in Norway. Many can be saved as long as they get to the hospital fast enough. This can be surprising for most people because stroke is considered something that only affects the elderly.
As we mentioned above, there are a wide range of potential side effects, and some can be very serious. Most people who suffer from stroke will suffer from psychopathologies that arise from the perception of loss of functional abilities. These changes can actually end up being more debilitating than the physical side effects of the stroke.
The most common types of emotional changes
- Pathological emotion or pathological laughter or crying. This is when a patient laughs or cries disproportionately at the stimulus that triggers said reaction.
- Emotional incontinence. This is related to the previous point, as it refers to difficulties in regulating and expressing emotions. The emotional response may be disproportionate or inappropriate in terms of frequency, intensity and duration. They can also be completely out of context.
- Fatigue after stroke. Intense exhaustion from minimal mental or physical exertion. It can be accompanied by a subjective feeling of exhaustion. Some people also have trouble starting tasks that require some kind of effort, however minimal as it may be.
- Catastrophic reactions. A person with this condition may also have other symptoms of depression.
- Apathy. Loss of interest in things, people and activities.
- Anosognosia. Lack of awareness of the disease. The most noticeable thing about this particular symptom is the emotional indifference of the disabled person.
- Irritability and aggression. This is very common. It can be verbal or physical (against objects and people).
- Anxiety or depression. These are very common after any kind of brain injury. However, a stroke always involves some form of loss of function or loss of ability. This means that patients must experience the grieving process, which can cause depression and anxiety regardless of the injury itself.
These symptoms vary from person to person and can be difficult to diagnose. Nevertheless, the medical system should have adequate procedures to ensure the timely detection and intervention of stroke patients.
Secondary behavioral changes after stroke
- Changes in social behavior. This is the most common change and may include the rest. Those who are close to the patient tend to observe that they are not the same. They notice changes in character, personality, the way they treat others, etc.
- Infantilism. The tendency to act irresponsibly and naively.
- Inflexibility. This is another of the main symptoms. It refers to the inability to change already made plans. A reduction or lack of working memory can cause this symptom.
- Selfishness. Stroke patients are often egocentric and unable to put themselves in the situation of others.
Adaptive social behavior requires an understanding of the views of others. This ability is called mentalization. The lack or reduction of this ability means that you can not understand the people around you or their needs. This obviously causes a lot of problems in relation to others.

The importance of coping with emotional and behavioral changes
As you can see, the emotional and behavioral changes are natural reactions to the stroke. However, they can have negative consequences for the patient’s recovery. A good attitude and motivation are crucial for success in the rehabilitation process. It goes much faster and more positively if the patient is cooperative and willing to do what is necessary.
With that in mind, the patient should ideally go through neuropsychological rehabilitation as well as neurological rehabilitation. Patients and their immediate family members should also receive psychological attention to ensure that these emotional and behavioral changes are not an obstacle to recovery.
To conclude, it is also important to be aware of the emotional state of patients’ families or primary caregivers. Caring for a stroke patient can be overwhelming and often affects the psychological health of caregivers. Ensuring that they are healthy and have the resources they need is crucial for their own well-being and for the well-being of the stroke patient. After all, there is no better way to take care of others than to take care of yourself. As the saying goes, you can not pour from an empty cup.









